- Developer Help
- Help
Connect generic consumer
HITS environment
To be able to connect your consumer to HITS you must obtain an account on HITS. Apply on the Welcome page for an account.
Figure 1: SIF3 HITS Database View
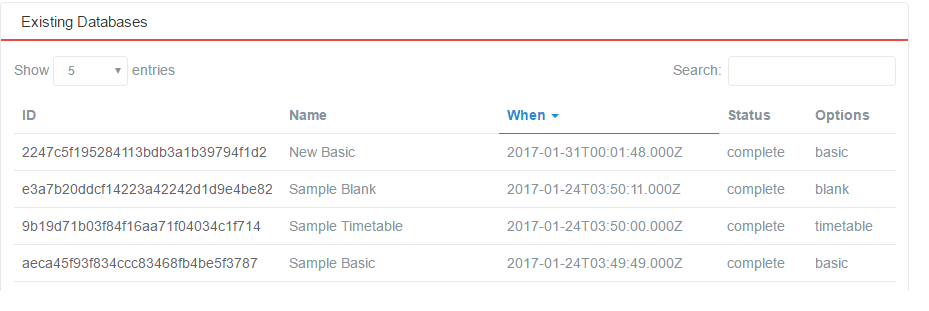
Select an existing database to see the Information page of that database, which contains SIF Environment information. The second part of that page looks like this:
Figure 2: SIF3 HITS Environment Page
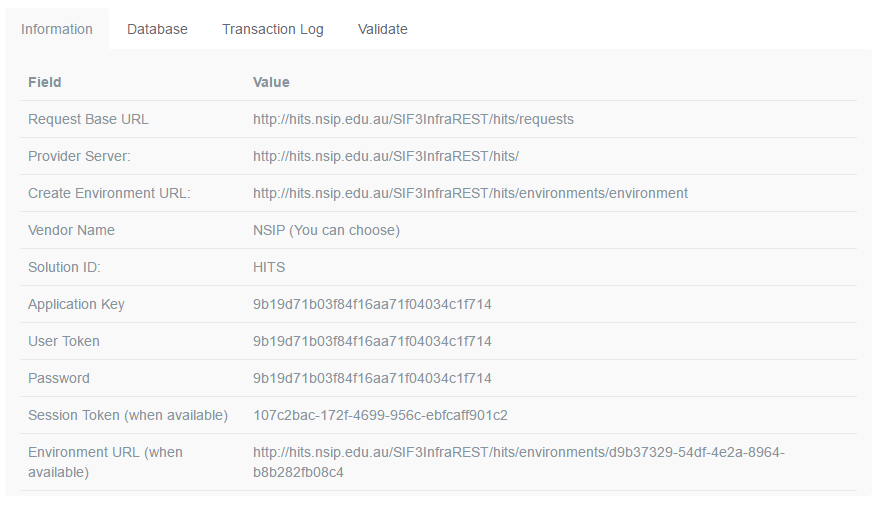
Configure REST Client
To configure your REST client to connect to your HITS environment, follow the steps below: (refer to SIF specifications for more detailed information.)
Step 1
Note: If the Environment URL and Session Token are already available from the dashboard, Steps 1–3 can be skipped.
Create an environment request payload.
The payload will populate the following XML template:
<environment xmlns="http://www.sifassociation.org/infrastructure/3.1"> <solutionId>HITS</solutionId> <authenticationMethod>Basic</authenticationMethod> <instanceId/> <userToken/> <consumerName></consumerName> <applicationInfo> <applicationKey></applicationKey> <supportedInfrastructureVersion>3.1</supportedInfrastructureVersion> <dataModelNamespace>http://www.sifassociation.org/datamodel/au/3.4</dataModelNamespace> <transport>REST</transport> <applicationProduct> <vendorName>Systemic Pty Ltd</vendorName> <productName>Test Driver</productName> <productVersion>0.1alpha</productVersion> </applicationProduct> </applicationInfo> </environment>
Obtaining the following from the Information page:
- Put the value of the “solutionId” into the <solutionId> node.
- Put the value of the “User Token” into the <userToken> node.
- Put the value of the “Application Key” into the <applicationKey> node.
- You can change the values under the <applicationProduct> node to any value applicable to you. Leave everything else as is.
Step 2
Create the authentication token for the initial environment request. Under HTTP Basic Authentication, this is done as follows:
- Create the consumer token: this is the Value of “Application Key”, followed by colon, followed by the Value of “Password” from Figure 2. For this example, it would be 9b19d71b03f84f16aa71f04034c1f1714:9b19d71b03f84f16aa71f04034c1f1714
- Base-64 encode the consumer token
- Prefix the Base 64 encoding of the consumer token with “BASIC ”
The procedure under HMAC SHA-256 to generate an authorisation token is as follows:
- create a timestamp in ISO-8601 format eg. 2017-02-27T09:48:42.942Z
- take the string ApplicationKey:timestamp and hash it using HMACSHA256 with the Password as the key, then base64 encode this hash. ApplicationKey and Password are from the Information page; timestamp is taken from the previous step.
- Base64 encode the string Sessiontoken:Base64EncodedHash, where SessionToken is from the Information page, and Base64EncodedHash is taken from the previous step.
- Prefix the result of the previous step with “SIF\_HMACSHA256 ”.
Step 3
Post the environment body payload, authenticated with the authorisation token, to the URL named in *Create Environment URL* from the Information page.
- Under BASIC HTTP authentication, the resulting token is included in the HTTP header of the POST to the URL, as the Authorization: field contents.
- Under HMAC SHA-256 authentication, the resulting token is included in the HTTP header of the POST to the URL, as the Authorization: field contents, and the timestamp value derived above is included in the HTTP header, as the timestamp: field contents.
Step 4
Your client should now be authorised to interact with a new defined environment. The Information page should now display a “Session Token” and “Environment URL” value.
Step 5
- Read the Request Base URL from the Information page. That is the base of the URL to which you will be addressing your REST queries.
- Suffix to the Request Base URL the name of the object you wish to access, followed by “s”; e.g. "http://hits.nsip.edu.au/SIF3InfraREST/hits/requests/SchoolInfos/"
Step 6
Create an authorisation token for the REST query.
Under BASIC HTTP authentication, the same token will be used for all interactions with the server.
- Read the Session Token from the Information page. This is used for the basis of the authorization value to be included with all subsequent interactions with the Environment URL.
- Read the Password from the Information page. This is used for the basis of the authorization value to be included with all subsequent interactions with the Environment URL.
- Concatenate the Application Key and the Session Token, separating them with a colon.
- Base-64 encode the resulting token
- Prefix the Base 64 encoding of the consumer token with “BASIC ”. This is the authorisation token.
Under HMAC SHA-256 authentication, each authorisation token is timestamped, so there is a different token for each post.
- create a timestamp in ISO8601 format e.g. 2017-02-27T09:48:42.942Z
- take the string SessionToken:timestamp, and hash it using HMACSHA256 with the Password as the key, then base64 encode this hash. ApplicationKey and Password are from the Information page; timestamp is taken from the previous step
- Base64 encode the string SessionToken:Base64EncodedHash, where SessionToken is from the from the Information page and Base64EncodedHash is from the previous step.
- Prefix the Base 64 encoding of the consumer token with “SIF\_HMACSHA256 ”. This is the authorisation token.
Step 7
Use the authorization field to authenticate all SIF REST queries, addressing them to the Environment URL suffixed with the plural object name.
Under BASIC HTTP authentication
- The authorisation token is included in the HTTP header for all subsequent queries, as the Authorization: field contents
- authenticationMethod with the value BASIC
- Alternatively, the request parameter access\_token can be included in the request, with the authorisation token as its value (without the BASIC prefix)
Under HMAC SHA-256 authentication
- The authorisation token is included in the HTTP header for all subsequent queries, as the Authorization: field contents
- Send a header "timestamp" with the value of timestamp from above.
- instead of headers you can also send your requests with the following request parameters :
- timestamp with the value of timestamp above
- authenticationMethod with the value SIF\_HMACSHA256
- access\_token with the last base64 value from above (without the SIF\_HMACSHA256 prefix)